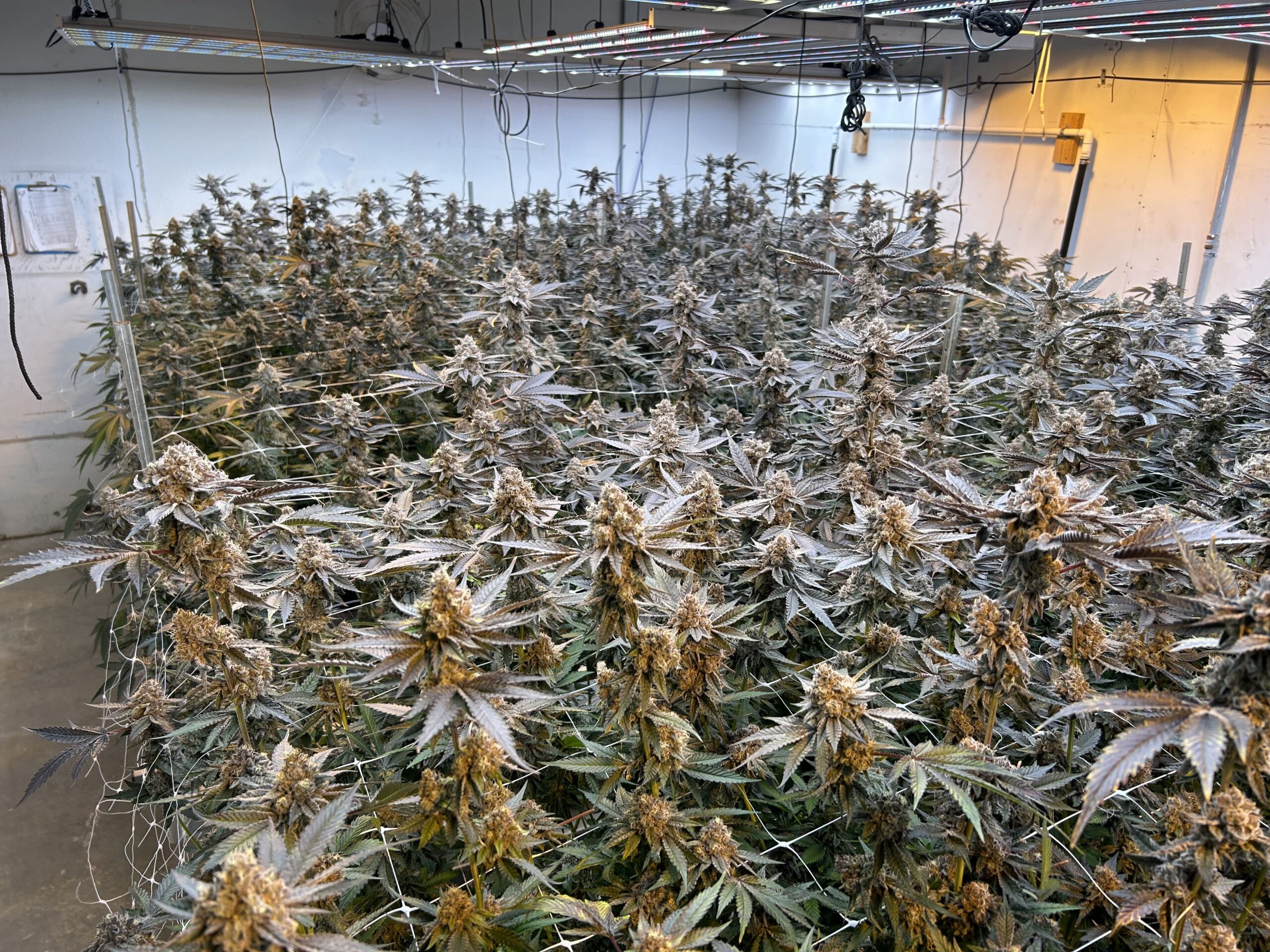
Cannabis inventory management is a practice that supports production planning and the company’s ultimate success in reaching their revenue goals. Vertically integrated cannabis companies that grow and manufacture products rely heavily on accurate inventory data in order to meet their input requirements for production goals. Without accurate inventory data, a complex operation will suffer and final numbers may be skewed or inaccurate.
Cannabis inventory management is also a necessary practice for compliance with state cannabis regulations. Metrc reports a licensee’s inventory data to the state. What’s entered into software can differ from what’s physically in the facility. With many cannabis businesses containing thousands of plants at a time, managing this volume of inventory manually can result in large data discrepancies. And in the highly regulated cannabis industry, this can mean hefty fines or even license suspension.
RFID vs Barcode Scanning
RFID tags contain microchips that allow a reader to scan for data and update tag data via radio frequency signal. Barcode scanners, on the other hand, require manual scanning of each tag.
As with any efficiency measures, detailed processes are the key to managing inventory well. Cannabis inventory management tools like RFID tech and barcode scanners are helpful in recording plant tag data. Unfortunately they’re not the end all be all. At the end of the day, cultivators must still physically count plant inventory if they wish to have real-time accurate inventory and reporting.
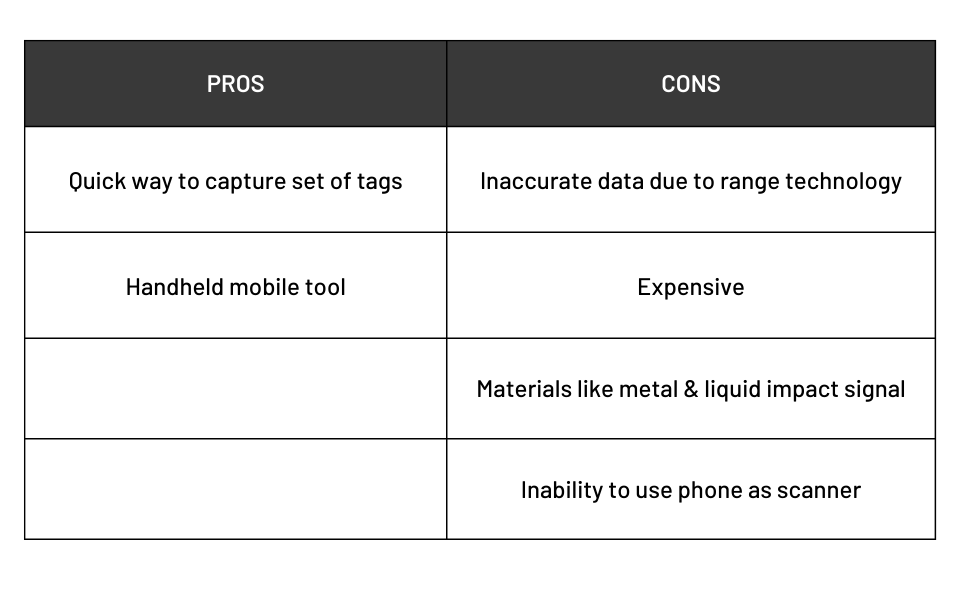
Pros and Cons of RFID
Cannabis RFID scanners are a widely debated tool in cannabis cultivation. The promise of substantial time savings from scanning a whole room in one second is obviously appealing. But often, the output is unfavorable for many growers. Sometimes plants aren’t tagged, sometimes there’s more than one tag on a plant. As an inventory manager, that’s not reliable enough to execute a stock count or perform a reconciliation.
Cultivators also find that metal and liquid interfere with radio frequency signals. Metal, for example, can deactivate the antenna on an RFID tag, preventing transmission. Liquid, like in grow room reservoirs, can impact the reliability of an RFID tag’s signal.
Here are the pros and cons to RFID that we’ve encountered.
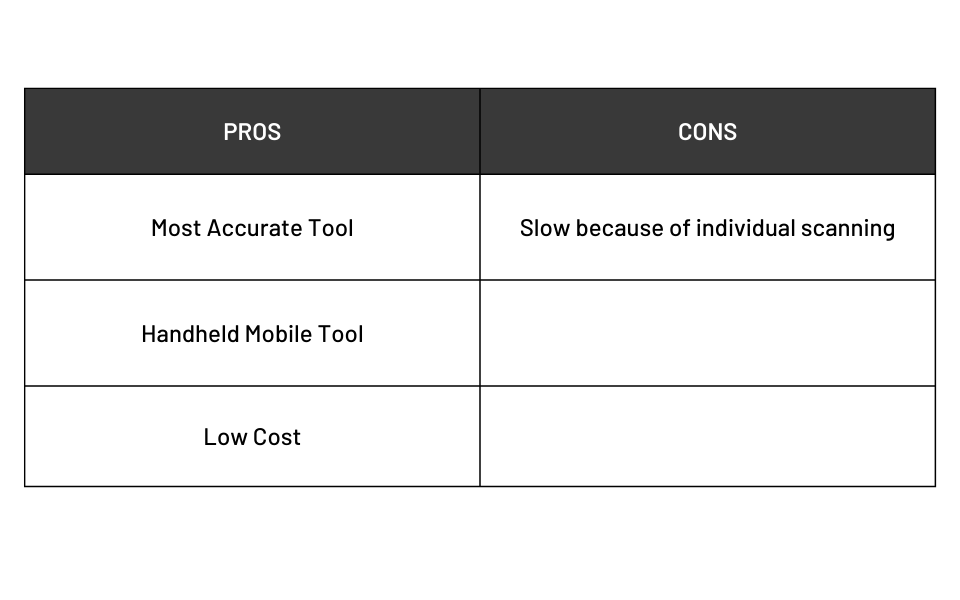
Pros and Cons of Barcode Scanning
The standard barcode scanner, on the other hand, is tried and true. While it requires a bit more time, the resulting data is more accurate.
While cannabis inventory management is a mundane, repetitive process, it’s critical to an organization’s production, compliance, and efficiency. We recommend a physical inventory audit twice per month. One strategy is to audit different zones on specific days. For example, the nursery can be audited every other Tuesday and Flower Room 1 can be audited every other Wednesday.
While an RFID scanner will get all the tags in the room, putting a set of eyes on every plant will ensure 100% accuracy. Your team may forget to destroy, waste or even apply tags to plants. So when a state auditor pays a visit, they’ll review the actual plants in the room to make sure the counts match up with your Metrc account. For this reason, we recommend regular inventory checks and reconciliations.
Cannabis Inventory Management Software
Scanners automatically load inventory data into compliance and cultivation management software, like Trym, help keep operations running smoothly. In Trym, teams can quickly see how many plants are in each room, what plants are in vegetative vs flowering stages, and the latest harvest data and waste numbers. Meeting production goals can be tricky, but with all the inventory data at your fingertips, the team can stay synchronized in cultivation operations.