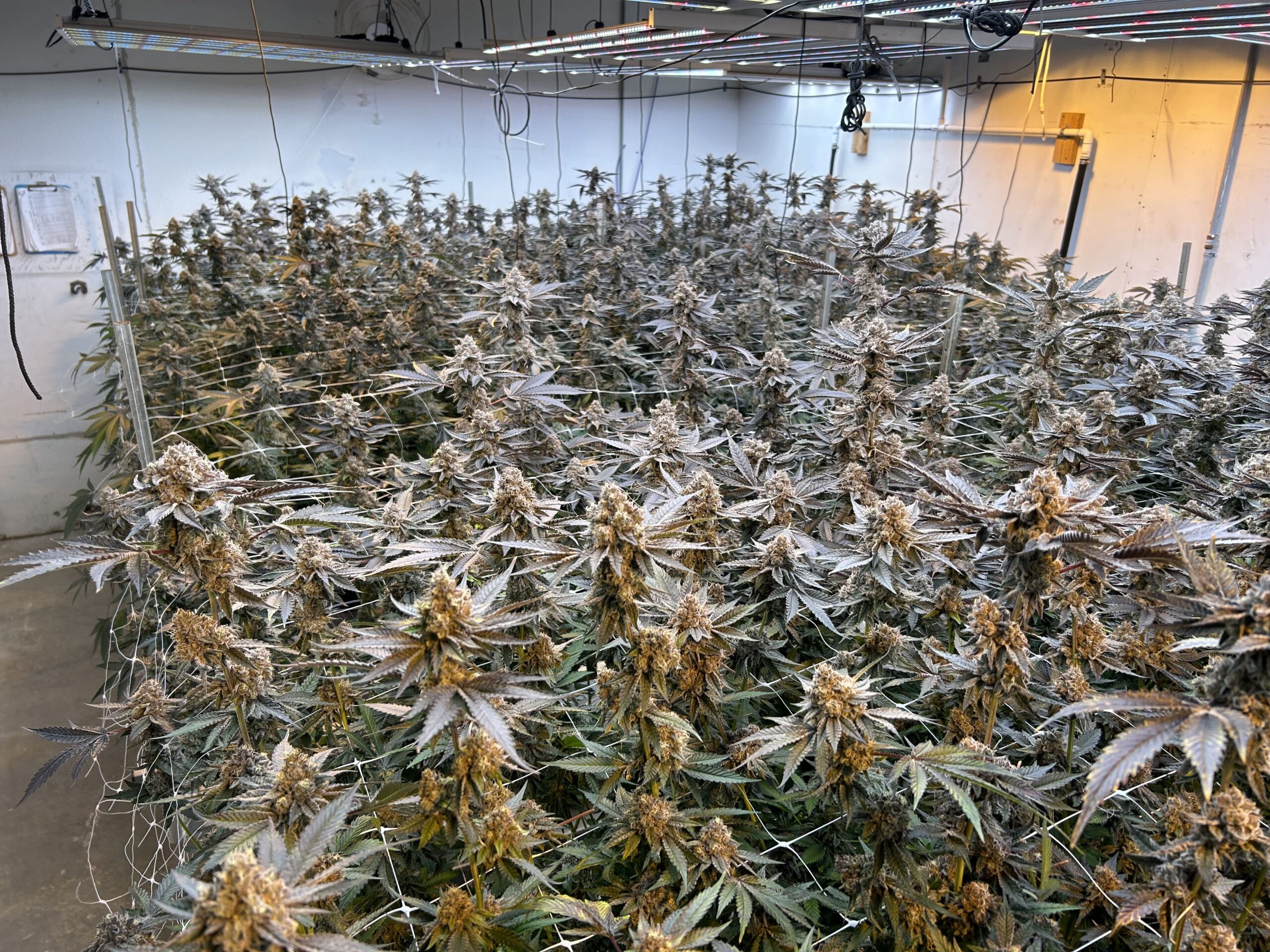
Recently, the concept of crop steering has become a popular topic among cannabis cultivators. While some growers are familiar with crop steering, many are just now starting to adopt the techniques. Unfortunately, there’s little information published on crop steering for cannabis cultivation.
In this post, we’ll introduce you to the concept of cannabis crop steering. For a deeper dive, download our Growers Guide to Crop Steering, which covers parameters and strategies as developed by leading industry experts.
Table of Contents
What is Crop Steering?
Cannabis plants have hormonal systems that regulate their growth in response to external stresses. The concept of crop steering is essentially the exploitation of these hormonal responses by manipulating a controlled environment to achieve a desired outcome – like bigger yields.
When a plant puts most of its energy into producing leaves and not much into flower formation, it is considered to be in vegetative growth. When a plant is focused on the development of flowers, it is considered to be in generative growth.
Growers must maintain proper plant balance, a defining concept in crop steering. The plant focuses on leaf and stem growth or flower production at any point in the life cycle. If the plant spends too much time in either, the plant balance will be skewed. And if the plant isn’t in balance, then it’s likely that production and quality will ultimately suffer.
The goal of commercial cannabis production is to maximize yields by optimizing plant growth in each stage. With crop steering, plants can produce only enough foliage and stems in vegetative growth to support vigorous flower production.
The Importance of Precision Crop Steering
Precision in crop steering transcends basic plant care; it’s about calibrating environmental factors to achieve the pinnacle of plant potential. This precision impacts not only the quantity but the quality of the yield, influencing factors like cannabinoid profiles and terpene expressions.
Cannabis is known for its sensitivity to environmental shifts, so the margin between optimal growth and stress is slim. Precision crop steering, therefore, becomes an art form as much as a science, requiring a deep understanding of plant physiology and environmental interactions.
Fine-Tuning for Optimal Yields
Going beyond the basics, precision crop steering involves an almost surgical approach to plant care. Each variable is adjusted based on the plant’s current state, anticipated growth patterns, and the final product’s desired attributes.
For instance, the precise timing of nutrient delivery and the light spectrum can be fine-tuned to enhance the secondary metabolites responsible for cannabis’s therapeutic and aromatic qualities, thus tailoring the final product to specific consumer preferences or medical efficacy.
The Delicate Dance of Environmental Accuracy
Precision crop steering is like a delicate dance where each step is planned and executed intentionally. For example, growers might introduce a slight, controlled stressor, such as a temporary increase in temperature, to enhance trichome production and thus increase the plant’s resinous output.
However, the stress must be carefully monitored and kept within a threshold to prevent adverse effects. This requires a deep understanding of the stress physiology of cannabis and a responsive approach to environmental management.
| Parameter | Impact on Cannabis |
|---|---|
| Irrigation | Roots development, nutrient uptake |
| Climate | Vegetative growth, hormonal responses |
| Lighting | Generative periods, vegetative stage |
How does crop steering work?
Crop steering operates on the principle of finely tuned environmental control to guide a plant’s energy allocation. By adjusting variables like light intensity, humidity, watering schedules, and nutrient concentrations, cultivators can nudge cannabis plants between vegetative and generative growth phases.
This intricate dance is orchestrated by manipulating the plant’s natural hormonal responses, fostering conditions that promote leaf and stem development or produce flowers. The precision of these adjustments is key, as the plants’ growth direction is highly sensitive to their surroundings.
The Science Behind Crop Steering
The science of crop steering is an intricate play of horticultural acumen and plant biology. It’s rooted in understanding how plants perceive their environment and subsequently allocate resources.
For instance, increased humidity and nitrogen availability might push a plant into vegetative vigor, while drier, potassium-rich conditions might encourage flowering. Growers exploit this by manipulating signals — such as light wavelengths and nutrient ratios — to coax the plants into the desired growth pattern, ensuring that the energy is directed where it’s most beneficial for the crop’s stage and health.
The Lever of Plant Development
In environmental control, every parameter is a lever that can be pulled to direct plant growth. It’s about creating a symphony of conditions that resonate with the plant’s growth phases. Sophisticated climate control systems can automate these conditions, adjusting them in real-time based on data and statistics from sensors that monitor plant responses.
This could involve increasing light intensity to increase photosynthesis during vegetative growth or tweaking CO2 levels to spur flowering to achieve a harmonious balance that promotes health and productivity.
The Role of Environmental Conditions in Crop Upbringing
Environmental parameters are the cornerstones of crop steering, delicately manipulated to guide plants through various growth patterns. Adjustments made to light, climate, and irrigation within indoor or greenhouse settings can lead to plants that not only grow bigger but also boast higher quality with improved yields. For instance, maintaining an optimal vapor pressure deficit (VPD) can help balance a plant’s need for both vegetative and generative growth, leading to healthy, high-yielding cannabis crops. See our guide to using a VPD calculator and chart.
Root zone management is integral to this process. It encompasses an irrigation strategy tailored to the precise needs of the crop, considering factors like water content, zone temperature, and electrical conductivity. Strategic application of crop steering principles can influence the vegetative and generative growth at any life cycle point, rather than being confined to predetermined growth stages.
The Influence of Nutrient Management on Crop Steering
The pathway to maximizing yields and achieving optimal bud quality lies in the adept management of nutrients. The selectivity and control provided by organic versus synthetic nutrient sources are distinct; organics tend to release more slowly, offering a gentle, steady feed, while synthetics render a more immediate, precise input. Environmental factors often weigh heavier in quality determination than the nutrient source itself. Striking the appropriate nutrient balance and ratio is critical to nurturing high-quality cannabis buds, spotlighting the pivotal role of nutrient management within the realm of crop steering.
A nuanced approach where plants are not completely flushed before harvest can help in maximizing yields, although a minimal flush with plain water is suggested to aid nutrient uptake efficiently.
Root Zone Management
Understanding the root zone is pivotal in mastering crop steering for cannabis. Irrigation strategies and substrate choices affect the root environment, which in turn influences overall plant health. Effective root zone management encompasses monitoring parameters such as water content, temperature, and electrical conductivity (EC) within the substrate. By deploying advanced sensors and technologies, growers gain invaluable insights into the root zone conditions, enabling precise adjustments that optimize nutrient uptake and enhance plant vigor.
The Impact of Irrigation Strategies on Crop Steering
The strategic implementation of irrigation strategies is crucial for successful crop steering. When steering generatively, balancing the increase in water uptake with the ensuing nutrient concentration becomes vital, as higher water intake can often lead to an accumulation of salts. This is observed in the gradual increase of pore EC readings over time. Conversely, vegetative steering, characterized by lower root zone pressure, leads to a slower rise in pore EC readings due to lower nutrient uptake and less water available for solute dilution.
The dry-back irrigation strategy is instrumental in promoting healthy root growth, whereas a consistent moisture approach tends to support vegetative expansion. By varying irrigation frequency, volume, shot size, and timing, along with efforts to maintain lower substrate electrical conductivity, cultivators can stimulate and maintain vegetative growth effectively. Through these nuanced strategies, manipulations to the water supply can substantially influence a plant’s growth trajectory and stress levels, framing irrigation as a powerful tool in the crop steering arsenal.
Check out our site visit to Pacific Growth to hear their crop steering journey:
Vegetative Growth
Vegetative growth is when stems and foliage are the predominant focus of the plant’s energy use and resulting growth. Generally speaking, mild growing conditions are best to stimulate vigorous leaf growth. Conditions that favor vegetative growth include lower electrical conductivity (EC), higher water content (WC), lower vapor pressure deficit (VPD), lower light intensity, and an overall stress-free environment.
Although cannabis vegetative growth is most notably associated with the phase between clone and flowering, vegetative cues can be used to nudge plants back into vegetative growth at any point in their lifecycle.
For instance, if you have compact, slow-growing flowering plants, you can use climate and irrigation cues to inspire vegetative growth and stretch the plants out.
Effective vegetative steering involves:
- Adequate light: Ensuring high-intensity but cool light mimicking spring and early summer conditions.
- Controlled climate: Maintaining higher humidity levels to reduce water stress and encourage transpiration.
- Irrigation management: Frequent watering that keeps the substrate moist but not oversaturated to promote root exploration and health.
By carefully modulating these factors, growers can accelerate the vegetative growth rate and enhance the overall health and robustness of their plants. This sets the framework for a successful generative phase with potentially increased yields and quality.
Generative Growth
In generative growth, the plant’s energy is directed toward flower production. The plant slows down the growth of new foliage and reduces its stretching.
In contrast to the mild conditions that inspire vegetative growth, harsher summer-like conditions are the foundation of generative cues. Higher light intensity, lower substrate water content, higher EC, and higher VPD are all examples of ways to motivate generative growth in your crop.
Generative growth cues can be leveraged throughout the plant’s life cycle, not just in the flowering period. For instance, if you have plants in your veg room that are demonstrating signs of excessive vegetative growth, you can modify your climate and substrate to steer your plants to grow more generatively.
Key aspects of generative steering include:
- Light manipulation: Adjusting to a shorter daylight cycle that signals plants to begin flowering.
- Humidity and temperature: Creating slightly drier and cooler conditions to replicate the late season’s environment, helping plants to focus their energy on flowering and bud production.
- Irrigation and nutrition: Modulating the frequency and concentration of water and nutrient solutions to slightly stress the plants, thereby encouraging reproductive growth instead of vegetative expansion.
By implementing these generative cues, growers can effectively stimulate their cannabis crops to enter the flowering phase, facilitating the shift of the plant’s energy from foliar and root growth to the development of reproductive structures, thus achieving potent, aromatic, and cannabinoid-rich flowers.
Vegetative vs Generative Growth
It’s important to understand the difference between generative and vegetative growth because cannabis plants are either in one or the other at any given time.
When a plant puts most of its energy into producing leaves and not much into flower formation, it is considered to be in vegetative growth. When a plant is focused on the development of flowers, it is considered to be in generative growth.
To maintain proper plant balance, the plant focuses on leaf and stem growth or flower production at any point in the life cycle. If your plants are not balanced, they will ultimately suffer from lower yields due to less-than-optimal vegetative conditions. Crop steering allows the cultivator to nudge the plants between the two stages accurately to optimize their hormonal response and plant balance.
Matric Potential vs Osmotic Potential
Understanding the tug-of-war between matric potential and osmotic potential is crucial for effective crop steering. Matric potential refers to the force with which water is held in the soil or substrate. In contrast, osmotic potential pertains to the water’s movement driven by solute concentrations, such as nutrients in the solution.
In crop steering, the balance between these forces determines water and nutrient uptake. High osmotic potential can draw water out of the plant, favoring generative growth, whereas a favorable matric potential can encourage water intake for lush vegetative growth.
Water Retention and Nutrient Uptake
A more nuanced understanding of matric and osmotic potential reveals their impact on plant turgor pressure and overall vigor. Matric potential focuses on the substrate’s ability to hold onto water molecules against gravity, which is crucial in maintaining adequate moisture for roots.
Conversely, osmotic potential deals with the concentration gradient across the root membrane, driving nutrient and water absorption. Manipulating these potentials involves adjusting irrigation strategies and substrate composition, ensuring that plants receive hydration and nutrition without the stress of waterlogging or nutrient burn.
Matric and Osmotic Dynamics
Delving into the interplay of matric and osmotic potential, one finds a dynamic that dictates the plant’s day-to-day water and nutrient dynamics. Altering the substrate’s matric potential by changing its composition or moisture level can encourage roots to expand and seek water, enhancing vegetative growth.
On the other hand, manipulating osmotic potential by varying nutrient solution concentrations can influence a plant’s water uptake and is used to trigger stress responses that promote flowering. Be careful when increasing concentration to prevent unwanted nutrient burn.
When and How to Use Crop Steering
Crop steering can be done at any growth stage to accomplish a grower’s specific goals. In the last few years, crop steering techniques have really taken off at indoor cultivation facilities. Growers have been exploring a mix of vegetative and generative steering throughout the cannabis flowering cycle to maintain plant balance.
Growers use generative steering to initiate the flowering cycle with the change in photoperiod. Once flowers have set, and after around the first defoliation, they will switch to a vegetative strategy to keep the plant healthy and increase the bulking of flowers.
Some growers go back and forth between vegetative and generative techniques to maintain plant balance. Other growers maintain vegetative steering until the crop gets closer to harvest, then switch to a heavy generative steer to finish the crop.
You should experiment with these strategies on each cultivar as they will react differently to the timely changes in environmental conditions. The way to track the steering cues and their effects on your plants is through crop registration.
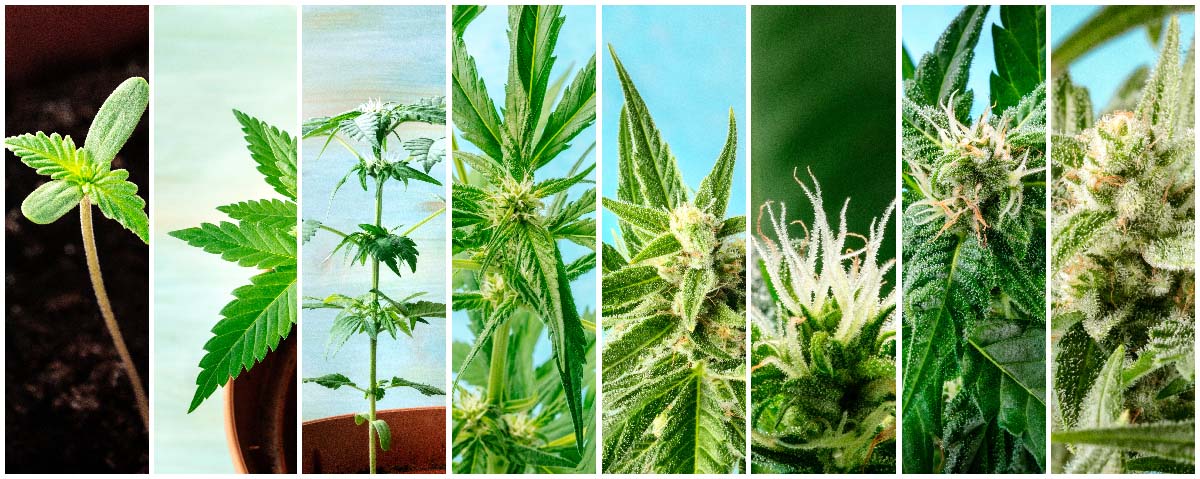
Understanding the Different Growth Stages in Cannabis Cultivation
The life cycle of a cannabis plant is divided into four main stages: propagation, vegetative growth, generative growth, and harvest. Each phase has unique requirements for water, light, and nutrients. During the vegetative stage, the focus is on developing a strong root system and robust plant structure, necessitating the careful management of water content to prevent substrate over-saturation.
As plants transition to the generative stage, energy shifts from root and foliage development to flower production. Here, the water content availability is adjusted to encourage the plant to utilize its reserves, thus driving flower growth. To initiate flowering, a typical light cycle shift to 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness is implemented, which closely aligns with the natural seasonal changes.
Developing a Crop Steering Schedule
Creating a crop steering schedule demands precision in altering plant growth and stress levels, particularly through water supply adjustments. Timing is vital to avoiding adverse effects such as wilting, especially during early development when the root system is vulnerable. Automated irrigation systems are integral to crop steering efforts, allowing growers to manage nutrient dosing, irrigation frequency, and volume with great accuracy.
Crop steering technology assists in maximizing the potential of each cannabis cultivar, providing optimal levels of volumetric water content and enabling precise drying back procedures. A calibrated crop steering schedule enhances quality and yield by directing plants to a balanced progression through their vegetative and generative stages.
Strategies for Environmental Control in Crop Steering
Strategic environmental control is the cornerstone of crop steering. By manipulating light intensity and photoperiod, along with fine-tuning climate conditions such as temperature and humidity, cultivators can influence how plants grow. Maintaining a balanced growth between vegetative and generative stages is critical to achieving high yields of healthy plants.
Irrigation management plays a fundamental role in environmental control. Techniques such as the dry-back strategy allow growers to modulate plant stress and growth by controlling water supply. Adjusting these environmental controls in harmony promotes a cultivation environment that is conducive to the plant’s developmental needs.
Optimizing Nutrient Ratios for Crop Steering
The selection of either organic or synthetic nutrients in crop steering is largely a matter of preference, as the main goal is to provide plants with the correct amounts and ratios of nutrients necessary for optimal growth. While organic nutrients are released slowly, synthetic options offer more precise control. Despite varied grower preferences, the key to quality bud production is ensuring the plants receive the appropriate nutrient balance.
Adjusting nutrient levels is essential to prevent buildup, which can lead to issues such as nutrient burn. Periodic flushing before harvest and the use of plain water can refresh the growth medium, enhancing yields. Optimizing nutrient ratios throughout the plant’s life cycle is pivotal in steering plants toward maximum productivity.
Effective Irrigation Techniques for Crop Steering
Tailoring the volume, frequency, and timing of irrigation events is a sophisticated aspect of crop steering. A dry-back strategy not only fosters root growth but also bolsters nutrient uptake. Conversely, maintaining consistent moisture levels supports vegetative growth and plant health. Substrate choice, such as rockwool with its low cation exchange capacity, can facilitate steerability through significant variations in water content.
Management of the root zone is crucial for successful crop steering. Careful selection of the substrate, combined with the strategic use of irrigation equipment and setup, underpins an effective strategy. Through meticulous planning and execution of these elements, growers can refine their irrigation techniques to promote the best outcomes in plant development and yield.
What’s happening in the Root Zone?
Cannabis roots play a vital role in the quality of the final product. Healthy roots sustain healthy growth, as the roots deliver water and nutrients to the plant. Root zone management is the consideration of irrigation strategy and the impact the strategy will have on specific properties in the root zone, such as water content (WC), temperature, and electrical conductivity (EC) in your substrate. Understanding each of these root zone properties and how changes will affect your plants is important.
Selecting a substrate is an important decision as it is a conduit for making water and nutrients available to the plant. Substrates like soil, coco mix, or rockwool cubes all perform differently as they have widely differing physical properties, such as the ability to absorb and retain water. To know how much to irrigate and feed your cannabis plants, it’s helpful to have root zone technology deployed that provides visibility into the conditions in your substrate.
Root zone technology, such as sensors, monitors the substrate temperature, EC, and WC. Monitoring your root zone will give you crucial information, which when combined with diligent crop registration practices, can help you answer key questions like “What dryback am I achieving overnight?”, “How high can I run EC before inducing crop damage?”, “What is the temperature of my root zone compared to the ambient temperature?”
Crop Registration
Crop registration is the collection of detailed measurements for your crop and is arguably the most important aspect of crop steering. Through diligent data collection, growers can track how their steering actions affect the plants and resulting yields. Common plant attributes that should be observed during crop registration are:
- Plant height
- Root development
- Stem diameter
- Internodal spacing
- Leaf color / Stem color
- Flower circumference
- Trichome attributes
- Plant vigor
By collecting data on these key performance indicators (KPIs) regularly, you can begin to make correlations about cause and effect. And ultimately, how potent, productive, or even how vulnerable a cultivar may be to disease and pests.
The Trym Approach
The Trym approach to crop steering is a fusion of technology with traditional horticultural expertise. Trym offers growers a granular view of their crop’s performance by leveraging data analytics and environmental monitoring tools. This approach isn’t just about adjusting the environment reactively; it’s about anticipating the plant’s needs and preemptively setting the stage for optimal growth.
By harmonizing technology with the plant’s natural rhythms, Trym seeks to streamline the steering process, ensuring each plant achieves its full genetic expression with every harvest.
Data-Driven Cultivation
Our mission at Trym is to empower cultivators with data analysis, using insights gleaned from every aspect of the growing process. For example, by analyzing data trends over time, growers can predict plant behaviors and adjust inputs preemptively. This might involve using software to track growth rates, feeding response, and nutrient uptake, then using algorithms to predict when a plant will enter a new growth phase and adjust environmental factors accordingly.
Proactive Crop Steering
The art of anticipation in the Trym approach means creating a cultivation plan that’s both reactive and predictive. By understanding the historical responses of their plants to certain conditions, growers can forecast needs and preemptively adjust the growing environment.
This might mean increasing certain nutrients just before the plant shows signs of deficiency or adjusting light schedules in anticipation of a growth phase transition. It’s a holistic approach that considers past, present, and future to keep the plants consistently in their optimal growth window.
Crop Steering Technology
Advancements and innovation in cultivation technology support the adoption of crop steering in the cannabis industry. Beyond data collection and analysis, growers can control and automate HVAC, lights, fans, irrigation, and fertigation systems. Through a combination of sensors, control systems, cultivation software, irrigation strategy, and crop registration, growers can now steer their crops to greater outcomes than ever before.
To dig deeper into the concept of crop steering and get guidance on implementing these techniques into your operation, download our Growers Guide to Crop Steering. Developed with leading industry experts, it will provide you with the knowledge and key parameters necessary to begin experimenting with crop steering!