Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has emerged as a transformative technology, reshaping inventory management across various sectors. The cannabis industry is no exception, with its unique challenges and regulatory intricacies. This article delves deep into RFID in cannabis operations, highlighting its advantages, challenges, and prospects.
What is RFID for Cannabis?
At its core, Cannabis RFID technology employs radio waves to track and identify objects. Unlike traditional barcodes requiring direct line-of-sight scanning, RFID tags can be read remotely, offering a faster, more efficient tracking mechanism.
This system comprises three main components: an antenna that scans, a transceiver equipped with a decoder to break down the data, and an RFID tag loaded with specific info. The antenna shoots out a radio-frequency signal detected by the RFID tag. The tag is prompted to share its stored data, which the antenna captures.
RFID seed to sale
RFID tags, embedded with microchips, can store pivotal data like the strain, origin, and cultivation history of the cannabis plant. This information can be transferred to Metrc directly or into a 3rd party cannabis software, like Trym, that reports all compliance events to Metrc on behalf of the user. The RFID seed to sale application enables commercial cannabis growers to quickly and accurately track the entire lifecycle of a plant, from seed to sale.
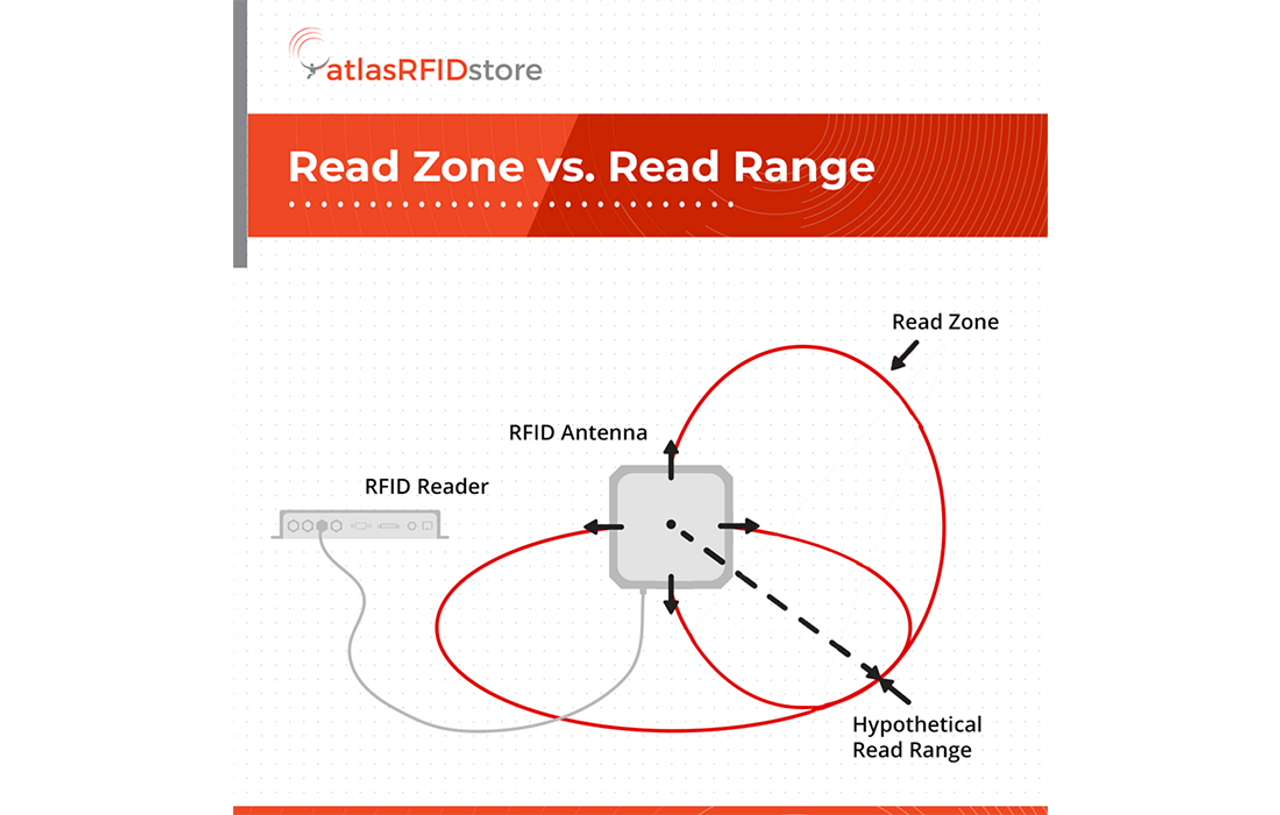
RFID enables:
- real-time inventory analysis,
- reduction in the potential for errors and
- allows for a quick and efficient product recall if necessary
RFID Technology in Cannabis and Why the Industry Needs it
RFID technology can help cannabis businesses easily ensure they’re always compliant with state regulations. Beyond that, RFID scanners support automated workflows that can significantly improve operational efficiency. And finally, operators can benefit from enhanced security through individual tags.
- Regulatory Compliance: With stringent regulations governing the cannabis industry, RFID technology provides a seamless way to ensure every product meets the required reporting and quality standards.
- Operational Efficiency: Gone are the days of manual tracking. RFID offers real-time insights, drastically reducing errors and streamlining operations.
- Enhanced Security: The risk of theft or diversion is reduced with individual tags for each plant and product.
The Practical Benefits of RFID in Cannabis
One of the most significant advantages of RFID technology in the cannabis industry is its ability to track individual plants and inventory items quickly and effectively. With RFID, cannabis operators can easily monitor thousands of plants in real-time, ensuring regulatory compliance and minimizing the potential for human errors.
By utilizing RFID tags, cannabis businesses can eliminate the need for traditional, manual scanning. RFID makes the entire inventory management process significantly faster and more efficient.
Why is Inventory Visibility So Important?
In any industry, but especially as regulated as cannabis, knowing precisely what you have on hand is critical. It’s not just about ensuring you don’t run out of stock; it’s about compliance, safety, and financial accuracy. Miscounts or misplacements can lead to many issues, like product losses or regulatory fines.
Product Recalls
One area in which RFID tech shines is assisting the cannabis business to identify affected cannabis material or products rapidly. This allows for targeted removal from shelves and timely communication with customers. Being able to respond and rectify the situation quickly is paramount.
Theft Prevention
Given how valuable cannabis products are, theft is always a concern for operators. But with RFID tags, every product has its own mini security guard. These tags keep tabs on each item, ensuring it stays on the right path. Any irregularity in the system is easily caught, making it less likely for things to go missing.
Automated Record-Keeping
Remember the days of scribbling notes on paper? We’ve mostly moved on from low-tech methods in the cannabis industry. They were a recipe for mistakes. RFID tech gives companies a crystal-clear picture of what’s happening while maintaining compliance with state regulations. Plus, it’s a huge time-saver!
RFID Benefits for Cannabis Cultivators
For cannabis cultivators, RFID technology offers several unique advantages that can significantly improve operations and compliance:
- Rapid Plant Location
- Streamlined Harvesting Process
- Auditing and Compliance
- Optimized Plant Care and Promotion
- Labor Efficiency
- Data-Driven Decision-Making
By incorporating RFID technology, cannabis cultivators can significantly improve their operational efficiency, ensure regulatory compliance, and gain valuable insights to drive business growth. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing such advanced technologies will be crucial for staying competitive and meeting the increasing demands of both regulators and consumers.
For cannabis cultivators, RFID technology offers several unique advantages that can significantly improve operations and compliance. One of the primary benefits is rapid plant location. RFID tags enable cultivators to locate specific plants within large grow operations quickly. Instead of manually searching hundreds or thousands of plants, staff can use RFID readers to pinpoint exact plant locations. This is particularly useful for identifying plants ready for harvest, locating plants that need attention (such as those showing signs of disease or pest infestation), and finding specific strains or phenotypes for breeding programs.
RFID technology can also streamline the harvesting process. Cultivators can quickly identify plants ready for harvest based on their RFID data, including planting date, strain, and growth stage. As plants are harvested, inventory systems can be automatically updated, and the harvested plants can be tracked through the drying, curing, and processing stages.
Another significant benefit of RFID technology is efficient auditing and compliance. Cultivators can conduct quick inventory counts without disturbing plants, generate accurate reports for regulatory compliance with minimal manual input, and easily track plant movement between different grow areas or facilities.
RFID tags can also help optimize plant care and promotion. By linking RFID tags to environmental sensors, cultivators can track individual plant conditions and use this data to fine-tune growing parameters for specific strains. High-performing plants can be easily identified for cloning or breeding programs, and genetic lineage and characteristics can be tracked for marketing and strain development purposes.
Labor efficiency is greatly improved with RFID technology. By automating many tracking and data entry tasks, cultivators can reduce time spent on manual plant counts and inventory management. This allows staff to be reallocated to more valuable tasks, such as plant care and quality control. Additionally, the simplified inventory procedures can minimize training time for new employees.
Finally, RFID systems provide a wealth of data that enables cultivators to make more informed decisions. Growers can analyze growth rates and yields across different strains, growing conditions, or cultivation methods. They can identify bottlenecks in the production process and optimize resource allocation based on real-time inventory data.
Challenges of Traditional Inventory Management Systems
Inventory management in the cannabis industry faces unique challenges. Many states require tagging individual plants as well as all finished products. Traditional systems rely heavily on manual tracking or scanning each tag. This method is error-prone, inefficient, and labor-intensive.
The manual method also makes tracking inventory across multiple locations difficult and requires a lot of paperwork and documentation. In addition, discrepancies in numbers can occur if employees forget to record data or fail to enter it accurately.

Labor Challenges in Inventory Tracking
The traditional scanning process requires a lot of time and manpower to record each plant or product. The old method doesn’t give businesses an up-to-the-minute view of their inventory on hand, which can slow down decision-making.
Tracking thousands of plants manually increases the risk of errors like miscounts or misplaced plants and/or tags. Bad data can jeopardize business compliance and be costly – legal penalties, fines, and even the loss of licenses.
Product Recall Challenges
Beyond the legal implications, there’s a consumer safety concern. Inventory mistakes can result in product recalls, eroding customer trust and harming brand reputation.
Product recall in the cannabis industry can be arduous and time-consuming. The complex regulations surrounding cannabis products require accurate and efficient recall management. Manual tracking can take a long time and delay action in an emergency scenario.
The Promise of RFID Technology
To address these challenges, RFID technology automates, simplifies, and ensures greater accuracy and compliance from cultivation to sale. By automating tracking, RFID reduces the chances of errors and offers real-time inventory insights. Plus, it can easily integrate with other software, further boosting the efficiency and accuracy of inventory management.
As the industry expands, embracing advanced tech becomes crucial to meeting changing regulations and staying ahead.
Overview of Seed-to-Sale Processes with RFID Technology
A seed-to-sale system with RFID technology offers a comprehensive solution to efficiently manage the entire supply chain. From the cultivation process to the sale of products, RFID technology enables real-time tracking and monitoring of every step. This level of visibility provides accurate and reliable data on inventory levels, plant growth, and product performance. It also provides a highly time-effective way to maintain state compliance.
Monitoring Actual vs. Expected Stock Levels
Complete inventory visibility is crucial for businesses to monitor and manage their stock levels effectively. To accomplish this, many operators are turning to RFID technology.
With instant access to inventory data, cannabis businesses can accurately track their actual stock levels and compare them to their expected ones.
Operators can identify any discrepancies or potential issues with their inventory, such as overstocking or stockouts, and make strategic decisions on how to fill the gaps or adjust production to reach their optimal levels.
Real-Time Data Collection
RFID systems offer a reliable way to document the chain of custody of cannabis products, reducing potential security issues and addressing concerns for both growers and consumers. By automating the scanning process, businesses can streamline inventory management and decrease potential errors, creating a more efficient and reliable system.
RFID systems can collect real-time data from plants, allowing cultivators to monitor their environment and identify potential problems before they become significant. This allows growers to respond more quickly to changes in temperature or other environmental factors that could potentially impact the quality of their product.
RFID Cannabis Tagging Techniques and Technologies
In the cannabis industry, RFID cannabis tagging employs various tag types and technologies to ensure product traceability and compliance.
Passive tags operate without a battery and are often used for their cost-effectiveness and simplicity. Active tags, albeit more expensive, offer longer read ranges and are suited for large-scale operations.
Another type of RFID tag is semi-passive, which means that a battery is used to power the circuitry while the RFID reader powers communication.
Types of RFID Systems
There are several types of RFID systems, including low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), ultra-high frequency (UHF), and microwave RFID. Each type operates on different frequencies and has specific characteristics.
Low-frequency RFID systems operate on frequencies ranging from 30 KHz to 500 KHz, with the typical frequency being 125 KHz. These systems have short transmission ranges, typically from a few inches to under six feet. LF RFID is commonly used for access control, proximity cards, animal tracking, and small object identification.
High-frequency RFID systems operate on frequencies ranging from 3 MHz to 30 MHz, with the typical frequency being 13.56 MHz. HF RFID can provide better data transfer rates than LF systems and has a longer transmission range, up to a few feet. This type of RFID is commonly used in applications such as payment cards, inventory management, library books, and electronic tickets.
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID systems operate on frequencies between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, providing even longer transmission ranges compared to LF and HF systems. UHF RFID is often used in supply chain management, asset tracking, and inventory management.
Microwave RFID systems operate on frequencies above 3 GHz, offering the longest read ranges of all RFID systems. These systems are often used in applications that require long-distance tracking, such as toll collection and vehicle tracking.
Choosing the right RFID tagging technique and technology depends on various factors, including the specific needs and compliance requirements of the cannabis business. When selecting an RFID tagging solution, it’s essential to consider factors such as read range, cost-effectiveness, and integration capabilities.

RFID Labeling for Cannabis
RFID labeling is crucial to implementing RFID technology in the cannabis industry. This process involves attaching RFID tags to cannabis plants, products, and packaging to enable efficient tracking and management throughout the supply chain.
Types of RFID Tags in Cannabis
The cannabis industry utilizes several types of RFID tags:
- Plant tags: These are durable, weather-resistant tags attached to individual plants or grow containers.
- Product tags: Applied to packaged cannabis products, including flowers, edibles, and concentrates.
- Shipping tags: Used on boxes or pallets for bulk transportation.
Information Stored on RFID Tags
RFID tags in the cannabis industry store a wealth of information, including unique identifiers, strain information, harvest dates, batch numbers, processing details, test results, and compliance data. This comprehensive data storage enables thorough tracking and management of cannabis products.
The Labeling Process
Cannabis businesses have several options for implementing RFID labeling. Automated labeling systems can be integrated into production lines for high-volume operations, while hand-held RFID printers are useful for smaller operations or on-demand labeling. Some cultivators incorporate RFID tags into their plant stakes or containers from the start of the growth cycle.
Compliance Considerations
RFID labels must meet state-specific requirements for information content and formatting. Tags should be tamper-evident to prevent unauthorized removal or alteration. Some jurisdictions require specific tag placement on plants or products, making it essential for businesses to stay informed about local regulations.
Environmental Factors and Durability
The cannabis industry presents unique environmental challenges for RFID tags. These tags must withstand various conditions, including high humidity in grow rooms and cold storage for certain products. For outdoor cultivation operations, UV-resistant materials are essential to ensure tag longevity and readability.
Integration with Seed-to-Sale Software
For maximum efficiency, RFID labeling systems should seamlessly integrate with tracking software like Metrc or third-party solutions like Trym. This integration ensures real-time updates of inventory and compliance data, streamlining operations and reducing the risk of errors.
Security Features
RFID tags used in the cannabis industry often incorporate advanced security features. These may include encrypted data storage on tags to prevent counterfeiting, as well as holographic elements or other visual security features incorporated into labels.
By implementing effective RFID labeling practices, cannabis businesses can enhance their inventory management, streamline compliance reporting, and improve overall operational efficiency. As the industry continues to grow, RFID labeling will play an increasingly important role in maintaining transparency and traceability throughout the cannabis supply chain.
Innovations and Future Developments in RFID Technology
In the future, we can expect to see a range of exciting innovations in RFID technology that will enhance its reliability and cost-effectiveness. One key development area is the integration of RFID with other technologies, such as sensors and wireless communication. By combining these capabilities, RFID systems can provide real-time data on factors like temperature, humidity, and location, opening up new possibilities for applications in industries such as healthcare, logistics, and agriculture.
Durable and Versatile Tags
Another promising innovation is the use of printed or flexible RFID tags. Traditional RFID tags are typically rigid and require adhesive or attachment methods to be affixed to objects. However, printed or flexible tags can be directly applied or embedded into various materials like packaging films or fabrics. This advancement makes it easier to tag items and enables a broader range of objects to become RFID-enabled. As a result, industries such as retail could benefit from enhanced inventory management with access to real-time tracking of individual items on store shelves.
New Antenna Designs Could Boost Range
The performance of RFID tags heavily relies on the design of their antennas. The antenna is crucial in determining where and how the tag can be used and how effectively it will perform. As the competition for RFID antenna design intensifies, we expect to see innovative designs emerging in the coming years. These advancements will likely result in antennas and inlays that offer increased range and improved functionality.
One of the key challenges that RFID technology faces is transmitting signals through refractive and absorbent materials such as metals and liquids. These substances hinder RF signal movement, blocking effective communication between tags and readers. However, researchers are diligently developing new antenna designs to overcome these challenges. For certain applications, having an antenna positioned above the object being tracked may prove sufficient to ensure signal transmission, even in cases involving metal or liquid barriers.
Greater Memory for Smarter Tags
With increased memory, smart tags have the potential to revolutionize asset tracking and management systems. By embedding intelligence into the tag, assets can become “smart,” capable of tracking their attributes and relaying that information without relying on external computer networks. This streamlines inventory management processes and enhances security applications, as the tags can autonomously monitor and report any changes or discrepancies in the asset’s location or status.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting RFID
While RFID technology offers transformation, it can come with specific challenges. The initial investment is significant, and integration with existing systems may require additional time and resources. However, the realized labor efficiencies have the potential to justify the costs.
When considering an RFID system, it’s essential to assess potential costs. This includes the initial investment in hardware and software, the cost of training staff, and any maintenance charges for running the system.
Additionally, recurring fees for cloud-based data storage and analytics may be steep. At Trym, these fees are baked into our software fees, making it as streamlined and cost-effective as possible for the operator.
Integration can also be challenging, especially if the existing system is outdated or inadequate to handle the new technology. In such cases, a complete system overhaul may be necessary.
Finally, security must also be considered, as RFID systems can store sensitive data that could be vulnerable to theft and misuse. Businesses must ensure their RFID systems comply with regulations and their security plan.
The Future of RFID in the Cannabis Industry
The cannabis industry is ripe for innovation, and RFID technology is at the forefront. The ability to track every plant from seed to sale in real-time ensures compliance and boosts operational efficiency. While traditional methods have their place, they often fall short in an increasingly complex and demanding industry.
The benefits of RFID are clear: complete visibility into inventory, reduced human error, swift product recalls, and significant gains in efficiency. As the cannabis industry continues to evolve, RFID technology may be a game-changer for those wanting to stay ahead of the curve and safeguard their supply chain’s integrity.
Appendix: Resources and Further Reading
For further exploration of RFID in the cannabis industry, resources such as technical guides on RFID technology, regulatory documents outlining compliance requirements, and industry reports on market trends and challenges are invaluable. Organizations like the National Cannabis Industry Association (NCIA) and the Radio Frequency Identification Journal offer insights into best practices, technological advancements, and regulatory updates relevant to cannabis businesses seeking to implement RFID solutions.
- RFID Journal: Offers articles and case studies on RFID technology applications across various industries, including cannabis.
- National Cannabis Industry Association (NCIA): Provides regulatory updates, best practices, and technology trends relevant to the cannabis industry.