Cannabis cultivation is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of the plant’s growth and development stages. One of the most critical stages of cannabis growth is the vegetative phase, where the plant focuses on foliage development and root growth. This article will explore the science behind vegetative growth and how cannabis plants grow and develop during this crucial stage. To learn more about other stages of growth, like the generative phase, read up on crop steering techniques and parameters.
Photosynthesis is a vital process that drives vegetative growth in cannabis plants. During this phase, the plant relies heavily on the energy produced by photosynthesis to fuel its growth and develop lush foliage. Additionally, other factors such as light, nutrients, and temperature play a crucial role in determining the success of the vegetative stage.
By optimizing these factors, growers can ensure their cannabis plants grow and develop healthy and robust foliage, setting the foundation for a bountiful harvest. So, let’s dive in and explore the science behind vegetative growth in cannabis plants.
The Importance of Vegetative Growth in Cannabis Cultivation
During the vegetative stage, the cannabis plant is focused on growing as much as possible. This stage comes after the seedling stage and before the flowering stage. During this time, the plant will grow taller and wider, develop its roots, and produce more leaves. It’s essential to have healthy vegetative growth because it sets the foundation for the plant’s overall health and size.
The vegetative phase is a time for the cannabis plant to focus on nutrient absorption through its roots. This root development period is critical for the plant’s ability to uptake water, nutrients, and oxygen from the soil, leading to an increased growth rate. The optimal growth conditions are crucial at this stage because they influence the overall development of the plant.
Healthy Veg Plants = Productive Flowering Plants
Healthy vegetative growth will lead to a larger yield and more potent plants. During this stage, the plant develops its stem and leaves, which will help it absorb more light during the flowering stage. If the plant doesn’t have enough time to establish its leaves, it won’t be able to produce as much energy during the flowering stage, which will lead to a smaller yield. Therefore, paying careful attention to the plant during the vegetative stage is crucial to ensure it’s healthy and thriving for the rest of its life.
Node Spacing
Nodes are the intersections where a branch unites with another or links to the plant’s main stem. It is at these unique points that a cannabis plant gives off key indicators of its gender, as well as signals the transition into the flowering phase.
Cannabis plants exhibit different characteristics, whether Sativa, Indica, or hybrid. The varying appearances should define how growers control node spacing during the vegetative stage. An example is improving and directing airflow under and through the plant, ensuring optimal growth and development.
Light Cycle
One critical factor to control the growth cycle of cannabis plants is the lighting cycle. Growers can determine when their plants will transition from the vegetative stage to the flowering stage. Light cycles play an essential role in cannabis production because the quantity and spectrum of light regulate the growth rate and timing of other plant development phases.

Understanding the Life Cycle of Cannabis Plants
The life cycle of cannabis plants can be categorized into two main stages: vegetative and flowering. The plant goes through seed germination and early growth stages during the vegetative stage. Providing the plant with 16-20 hours of light daily ensures optimal growth during this stage.
As the plant approaches the flowering stage, white hairs will appear on the female plants, while the male plants will produce pollen sacs. Plant size during the flowering stage is primarily determined by the plant’s genetics and the growing environment.
Growing from Seed
For those starting from seed, it all begins with germination, where the seed cracks open and the roots emerge from the soil.
Unlike many other plant species, cannabis plants can develop into male or female plants. Identifying the sex of cannabis plants at an early stage is critical. Determining the sex can be achieved by examining the nodes near the plant’s base.
Male cannabis plants produce pollen sacs, while female plants produce white hairs known as pistils at the location of the nodes. During the vegetative stage, the difference between the sexes may not be evident at first glance and might require closer observation. It’s crucial to prevent pollination by identifying the male plants early and removing them from the cultivation area.

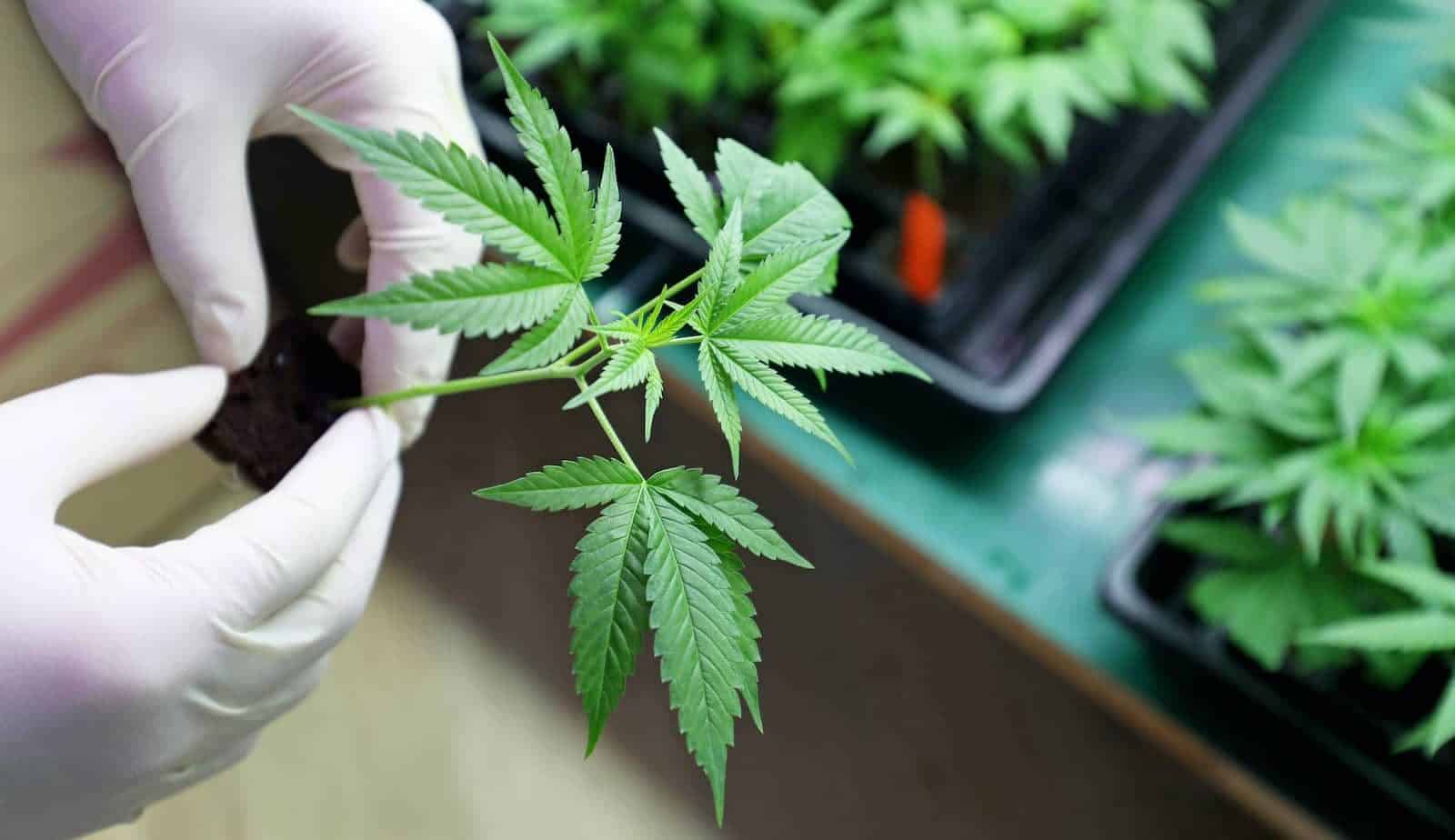
Clone Development
Cultivators who use clones instead of seeds work with a mother plant or purchase clones from a nursery. The clone typically includes a node or a section with one or more sets of leaves. Clones are placed in a suitable rooting medium, such as rockwool cubes, in a climate-controlled area to promote root development. Clones require consistent moisture and a stable environment to encourage root growth, usually taking 1-2 weeks.
Transplanting
Once the roots have developed sufficiently, clones can be transplanted and carefully moved to their new growing medium, ensuring they are not damaged. Regarding pot size, picking a pot that accommodates the plant’s growth is essential. The pot should have enough space for the roots to spread without being too large.
Once transplanted, the plant focuses on growing leaves and branches. It requires a consistent light cycle of 18-24 hours of light per day, along with proper nutrition and watering.
Factors Influencing Vegetative Growth
During the early stages of growth, the young cannabis plant requires the proper balance of light, temperature, and nutrients to establish healthy vegetative growth.
Growers can tell a plant is ready for the next stage when they develop their first set of true leaves. The vegetative stage typically lasts 2-8 weeks, depending on the container and desired plant size. During this time, the plant will continue to grow roots and establish a strong vegetative structure.
The Role of Photosynthesis in Vegetative Growth
Photosynthesis is critical in the early stages of a plant’s life, providing the necessary energy to establish a robust root system and develop healthy foliage.
During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants rely heavily on photosynthesis to produce enough energy to support their growth. This process involves converting light energy from the sun or artificial lighting into chemical energy, which is then stored in the plant’s leaves and used to fuel its metabolic processes.
Photosynthesis occurs in specialized structures within the plant’s cells called chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll – the pigment that captures light energy. As light strikes the leaves, it’s absorbed by the chlorophyll molecules, which then use this energy to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen ions.
The oxygen is released into the air, while the hydrogen ions are combined with carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce glucose – a type of sugar that provides the plant with the energy it needs to grow. Through this process, photosynthesis offers energy to the plant and helps regulate its internal environment by releasing oxygen and removing excess CO2.

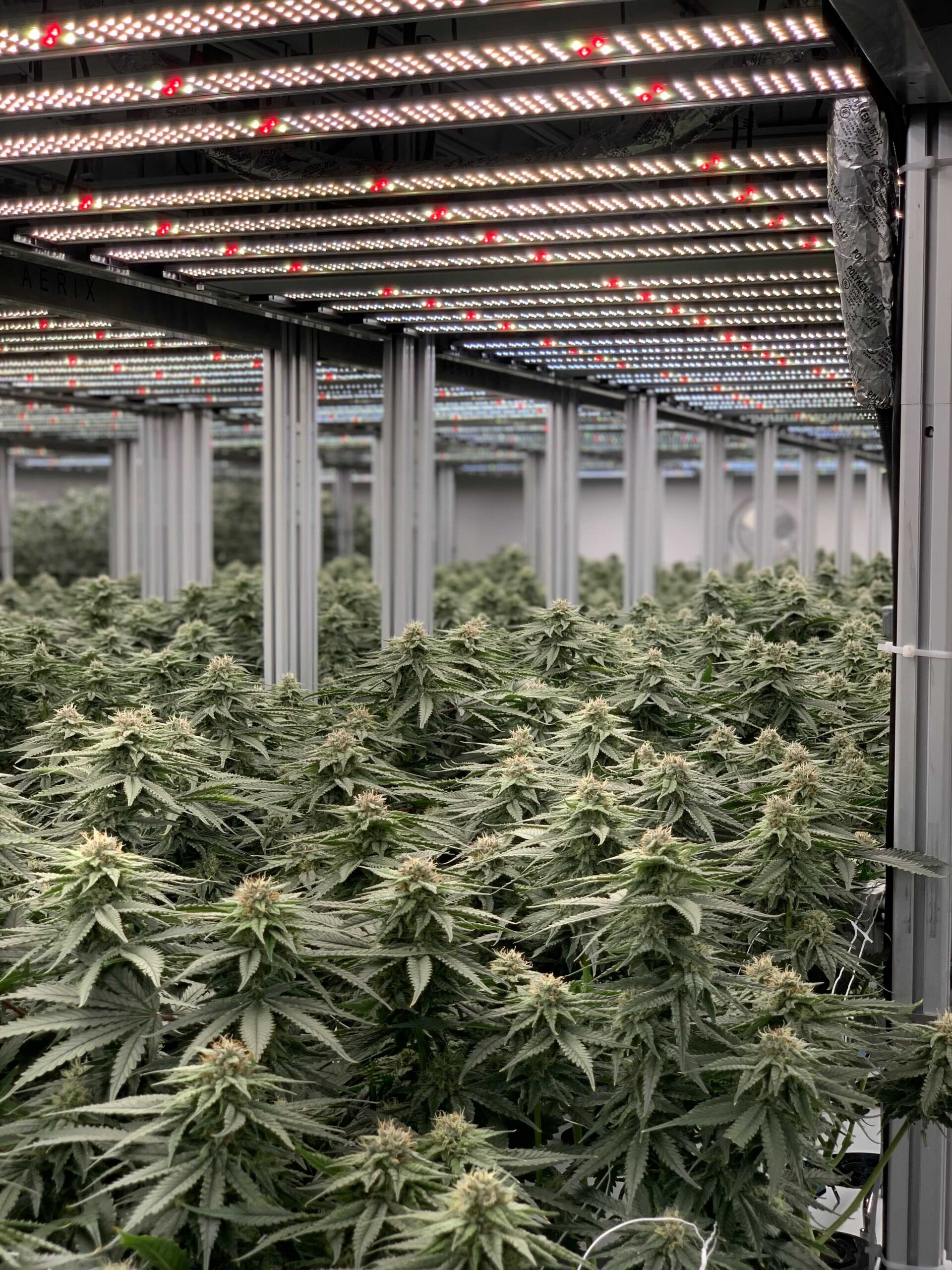
Light Requirements for Optimal Growth
Lighting is a crucial component in vegetative growth. One of the most important factors to consider is the hours of light a plant receives per day. Cannabis plants require at least 18 hours of light daily during the vegetative phase to promote healthy growth.
During the vegetative growth stage, cannabis plants require a different light intensity than they do during the flowering stage. Providing the correct amount of light is critical to the success of the plant’s entire life cycle, as it can significantly impact later stages of growth.
For optimal vegetative growth, it is recommended to provide the plants with gentle light levels of 400-600 PPFD (photosynthetic photon flux density) for 18-20 hours of daily light. PPFD measures the amount of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) that actually arrives at the plant.
This amount of light will allow the plants to photosynthesize at a healthy rate and produce sufficient energy for growth. Higher light levels can lead to stress that can cause growth to slow or even damage the plants.
Grow lights that are adjustable for light intensity and distance from plants will be quintessential in providing an optimal environment.
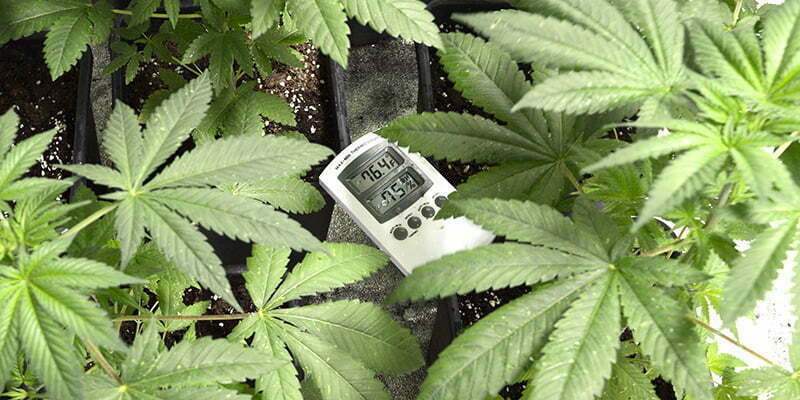
Temperature Range
Temperature is another vital factor in plant growth. The ideal temperature range in vegetative growth is a daily temperature range of 76 – 78°F and a night temperature range of 65 – 68°F. (Agrify)
Temperature extremes can cause the plant to become stressed and even lead to death. By monitoring temperature levels, growers can create the ideal, healthy, vegetative growth environment.
Using fans for air circulation to regulate temperatures and maintain optimal growth conditions is recommended. It’s crucial to avoid extreme temperature fluctuations as they may negatively impact growth or, in the worst case, kill the plant.
Nutrients
Nutrients play a crucial role in vegetative growth. The correct nutrients and soil pH level will support the plant’s development and ensure healthy growth. A pH of 6.0 to 7.0 in the root zone is ideal for early vegetative growth since it can boost nutrient uptake and absorption. However, the growing medium may dictate different pH ranges. The nutrient solution should be between 5.5-6.0 to keep the root zone pH optimal. When the Electrical Conductivity (EC) is too low, it can increase root zone pH. Read our in-depth guide on cannabis EC for more guidance and crop steering strategy.
Common Issues During Vegetative Growth
During the vegetative growth stage, cannabis plants undergo rapid growth and development. However, some common issues may arise during this period.
Slow growth, for one, can be caused by various factors like incorrect lighting, inadequate nutrients, or poor air circulation. Cold temperatures can also affect plant development, leading to stunted growth and reduced yields. Conversely, excessive heat can cause heat stress and damage to the plant.
Slow-Growing Cannabis Plants
Cannabis plants are known for their rapid growth rate, but sometimes, they may seem to grow slower than expected. There are various reasons why cannabis plants experience slow growth, including poor lighting, overwatering, inadequate nutrients, and improper temperatures.
Lighting
One of the most prevalent reasons for slow-growing cannabis plants is poor lighting. Cannabis plants require a particular amount of light to grow optimally. If they don’t receive enough light, they may grow slower or stop growing altogether. Placing the plants directly under a light source or installing additional grow lights can help increase their growth rate.

Overwatering
Overwatering can lead to slow growth or stunted growth in cannabis plants. Watering the plants frequently or too much can cause the roots to rot, negatively impacting their ability to absorb nutrients and leading to slow growth. To avoid overwatering the plants, water them only when the soil has dried out slightly. Proper soil drainage can also help prevent overwatering.
Nutrient Deficiency
Inadequate nutrients can also cause slow growth in cannabis plants. Nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are essential for growth and development, particularly during the vegetative stage.
Soil may not have enough of these nutrients, and adding fertilizers can help supplement the plants’ growth requirements. For those growing in a soilless substrate, the full spectrum of nutrients must be fed regularly so plants never starve for what they need.
Temperature
Another factor that can negatively impact the growth rate of cannabis plants is inadequate temperatures. If the temperature is too low, the plants may grow slowly or stop growing altogether. Keeping the plants in a warm environment is essential during the vegetative stage.
Humidity
Another factor is humidity, which can also influence the growth rate of cannabis plants. Although cannabis plants prefer high humidity during the vegetative stage, excessively high moisture levels can cause problems such as mold and mildew. Keeping the humidity around 60% in the vegetative stage is essential to avoid this.
Genetics
Some cannabis genetics may grow slower than others during veg. Certain Indica strains will remain short and compact even after a long vegetative stage. Slow growth doesn’t necessarily indicate a problem. (Dutch Passion)
To address slow growth in cannabis plants, growers should monitor the plants carefully. Look for yellowing or wilting leaves, which might indicate an underlying issue. Growers must adjust lighting, water and feed the plants properly, and maintain an ideal temperature range to enhance growth.
Effects of Cold Temperatures on Plant Development
Cold temperatures can harm cannabis vegetative growth, especially during the early stages of plant development. Exposure to low temperatures can lead to slowed growth rates and stunted plant size. Any deviation from the optimal temperature range can significantly impact the growth rate and development of the plant.
When cannabis plants are subjected to cold temperatures, they experience delayed seedling development and reduced overall growth. As a result, cold temperatures negatively affect the growth trajectory of cannabis plants, which directly impacts the maximum growth rate of the plants.

Exposure to low temperatures can also increase the risk of pests and pathogens that are typically less prevalent in optimal growth conditions. In particular, cannabis plants exposed to cold temperatures are more susceptible to mildew, mold, and root rot, decreasing plant health and yield.
To mitigate the adverse effects of low temperatures, growers must employ strategies that help the plant cope with cold temperatures. For example, adjusting the lighting schedules can help maintain a stable temperature within the cannabis growing space. By providing adequate daily light, growers can optimize nutrient uptake, assisting the plant to better cope with colder temperatures.
Maximum Potential Growth Rate and Size
During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants have the potential to reach varying sizes and growth rates. Various factors influence the maximum potential growth rate and size of these plants.
The most critical factor is the amount of light received by the plants. With the proper light cycle and hours of light per day, cannabis plants can experience maximum growth potential.
Another crucial factor is the plant’s genetics, which determines growth rate and size potential. Inherent in understanding maximum potential growth are phenotypic variations that can be picked out from germinated seeds or clones from different mother plants.
Phenotypic Variation Between Different Varieties
Phenotypic variation is observable between different varieties of plants, including their growth rate and biovolume. Research has shown that different varieties’ growth rates can vary depending on the treatment they receive. For example, some varieties may grow faster in cold temperatures while others may experience slow growth.
The interaction between genetic and environmental factors is a powerful driver of phenotypic variation. Genes determine the inherent traits of cannabis plants, which are then modified by environmental factors such as temperature, light, water availability, and nutrient levels. Combining these two factors results in distinct plant growth rates and production differences.
Research on Vegetative Growth in Cannabis Plants
When studying vegetative growth in cannabis plants, research often employs statistical tools and methodologies to better understand the underlying genetic factors and environmental conditions that influence plant growth.
Researchers use mixed models, genetic architecture, and variance analyses to tease apart the complex relationships between plant phenotype and underlying genetic traits and the effects of different growth conditions such as light cycle, temperature, and nutrients. Using these tools, researchers hope to identify the most desirable growth phenotypes and optimize growth trajectories for optimal yield and plant health.
Conclusion
Vegetative growth in cannabis plants is a complex process influenced by genetic and environmental factors. By understanding the science behind vegetative growth, growers can optimize their cultivation processes to maximize yield while ensuring plant health and quality. Research on these topics will continue to improve our understanding of this dynamic process, allowing us to better utilize the genetic potential of different varieties for optimized growth.